Dear Pat: I am planning to replace my current heating system with a geothermal heat pump. It is comparatively pricey to other options, but it seems like an efficient option, and I like the fact that it includes air conditioning. Would a geothermal heat pump be a good choice for me? — Ralph D.
Dear Ralph: In most areas of the U.S., space-heating and -cooling account for a large percentage of overall home energy use, so upgrading to a more efficient heat-and-air system is a great way to reduce your monthly energy bill. A geothermal heat pump, also known as a ground-source heat pump, is among the most efficient types of heating and cooling systems you can consider installing in your home.
Even when it is extremely hot or cold outside, the temperature a few feet below the surface of the ground remains relatively constant and moderate. A geothermal heat pump system uses this constant ground temperature to help heat and cool your home. As a result, geothermal heat pumps are quite efficient. For example, according to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, geothermal heat pumps use up to 44 percent less energy than traditional air-source heat pumps and up to 72 percent less energy than electric resistance heaters combined with standard air conditioners.
A geothermal heat pump system is made up of three main components:
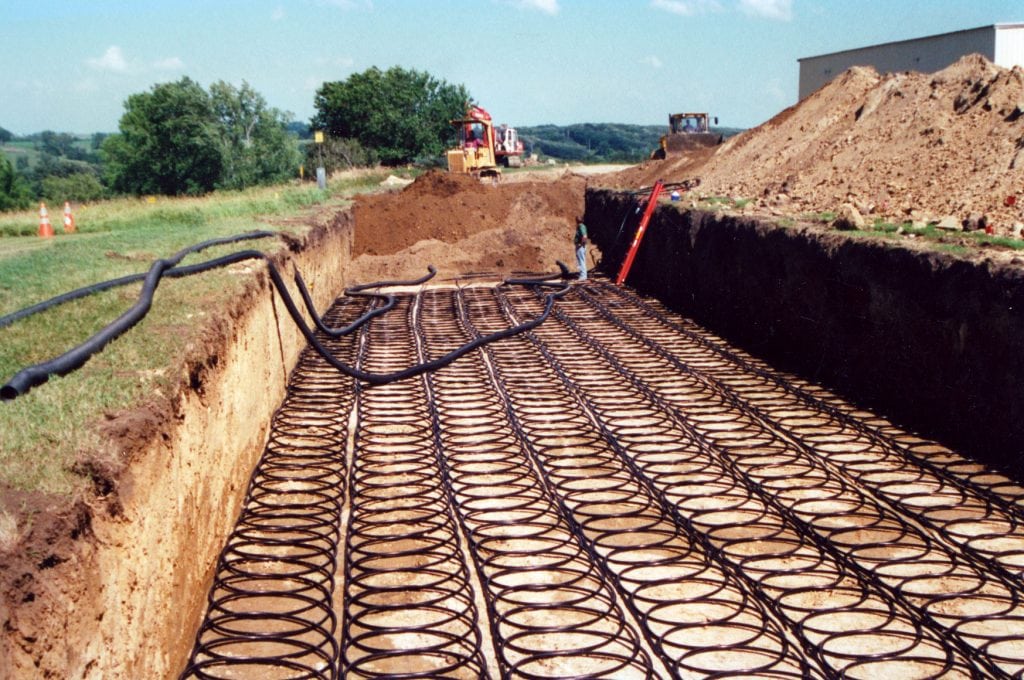
- The collector, or loop field, is in the ground and cycles a liquid like antifreeze through dense plastic tubing.
- The heat pump is in your home.
- The duct system distributes the heated or cooled air throughout your home.
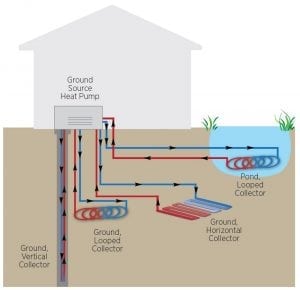
During the winter, the collector absorbs heat stored in the ground, and the liquid carries that heat to the heat pump, which concentrates it and blows it into the ductwork, warming your home. In the summer, the heat pump extracts heat from the home and transfers it to the cooler ground. The collector that exchanges heating and cooling with the ground can be set up in one of three main ways:
The collector that exchanges heating and cooling with the ground can be set up in one of three main ways:
- Horizontal system: Plastic tubing is placed in trenches 4 to 6 feet below the surface of the ground. This system works well when a home or business has sufficient available land because these systems may require up to 400 feet of trenches to be dug.
- Vertical system: If the site does not have sufficient space for a horizontal system, a collector can be placed vertically. In this system, a drill digs 100 to 400 feet below the surface and places the tubing. This system can be more costly than a horizontal system but will have less impact on any existing landscaping and can be used on smaller lots.
- Pond system: If a home has access to a pond or lake, a pond system (also known as a water-source heat pump) may be possible. The loop field is connected to the heat pump and then placed at least 8 feet below the surface of the water. If a homeowner has access to a pond that is sufficiently wide and deep, this can be the lowest-cost option.
Geothermal systems typically cost more than other heating systems largely because of the collector and the associated digging or drilling, but their high efficiency can help reduce the payback time. The cost will vary based on whether new ductwork is needed and the type of collector you install, among other factors. However, there are incentives available for those who install qualified geothermal heat pumps. Most notably, there is a 30-percent federal tax credit for installing an ENERGY STAR-rated system before the end of 2016 — so, if your system and installation cost $20,000, you could take $6,000 directly off your federal tax bill.
For those with high energy bills resulting from heating and cooling, an efficient geothermal system is a good option to consider. In addition, those building new homes should consider at the outset whether to install a geothermal heat pump. With new construction, the system can be included in the mortgage, and installing it before the home is completed means no disruption to your landscaping.
Talk with a qualified energy auditor who can help you evaluate the different heating and cooling options that would be best for your home.



